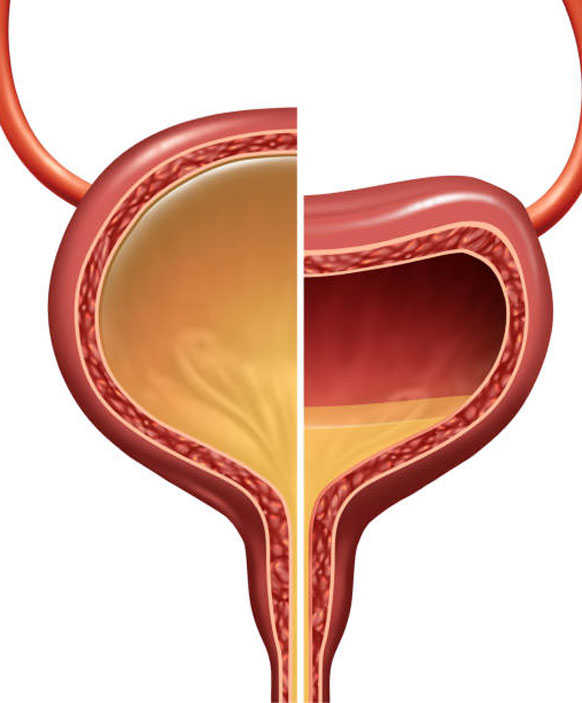
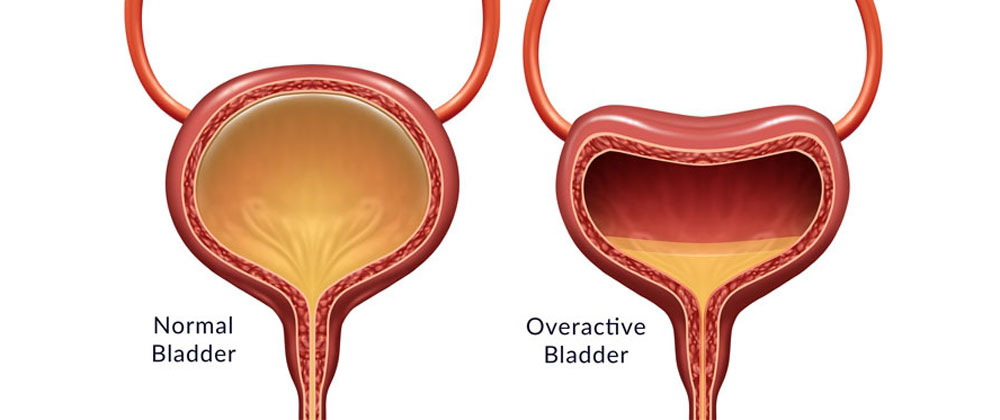
Overactive bladder is a medical condition in which a person has a sudden & frequent urge to urinate that is often difficult to control. It can occur any time of the day or night and often leads to urinary incontinence (loss of urine). Overactive bladder mostly occurs in women but can be seen in men as well. Ageing and diabetes are the most known causes and risk factors of an OAB.
An overactive bladder can be emotionally distressing as its symptoms can cause a lot of embarrassment to the patient. It makes you feel uncomfortable or limits your work, and drastically affects your social lifestyle. It can also cause depression and anxiety due to limited socializing and isolation. It may also disrupt your sleep and cause insomnia.
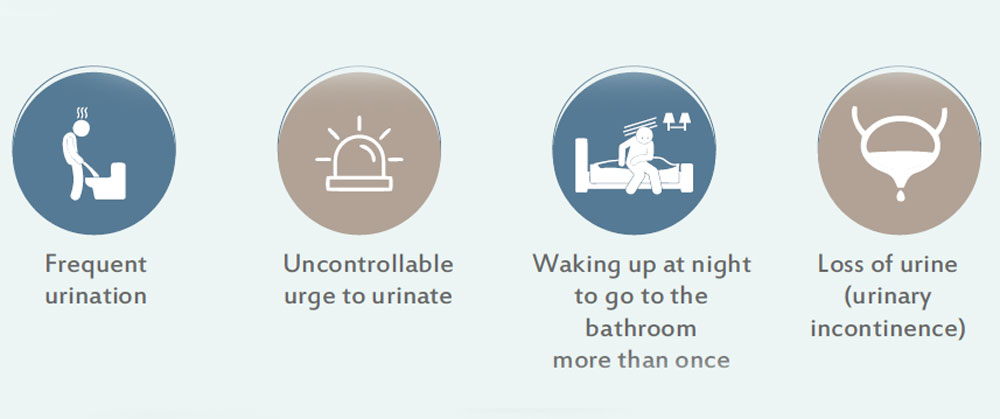
The main symptoms of an OAB
Causes of OAB
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Neurological disorders
- Diabetes
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Abnormalities in the bladder
- Enlarged Prostate
- Excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption
- Cognitive decline due to aging
- Certain Medications
- Incomplete bladder emptying
Can OAB be prevented?
The following are a few simple lifestyle choices that can significantly lower your risk of an overactive bladder.
- Maintain a healthy Weight
- Get Regular, daily physical activity & exercise
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Quit Smoking
- Manage Chronic conditions, like diabetes, better
There are various treatments such as pelvic floor exercises and therapies, maintaining a healthy life, using absorbent pads, and bladder training. At times, doctors prescribe medications to relax the bladder and soothe the symptoms of OAB. In most situations, your doctor might recommend you have a fibre-rich diet and stool softeners to avoid constipation and have small amounts of water at different intervals of time. You will also be asked to cut down your caffeine habits like coffee, cola, etc., and alcohol as well.
Bladder injections are also a type of treatment recommended in OAB; these injections are also called Botox and are used in small doses, injected directly into the bladder tissues to relax the muscles.
There are also surgical interventions which may involve increasing the capacity of the bladder or complete removal of the bladder.